【动机】
众所周知, linux shell 编程, 非面向对象, 故以下代码无法运行:
Person(){
local name age career
ctor(){
name=$1
age=$2
career=$3
}
say_hello(){
aop tip center "hello, my name is $name, I am $age years old, I am a $career."
info "these are other parameters:<$1>,<$2>,<$3>..."
}
}
clear
local p=$(new Person "John williams" 69 "guitar artist")
p.say_hello one two three
如何让它正常运行?
【意图】
利用上一篇动态函数的科学实现提到的 command-not-found.sh 模块, 把 new 对象, 以及点操作符等面向对象的特有调用重定向为 linux shell 可执行的操作.
【预备函数】
在 data.sh 中, 新建函数 ensure_par:
:<<COMMENT
确保给定的路径(可能是目录或文件, 不论存在与否)的父目录存在.
参数:
$1: 给定的路径
返回: 无
注意: 根目录 / 的父目录, 仍然等于 / .
COMMENT
ensure_par(){
local par=$(dirname "$1")
[ ! -d "$par" ] && mkdir -p "$par" || :
}测试略.
【实现】
新建模块文件 oop.sh, 写入以下代码:
#!/bin/bash
:<<SUMMARY
本模块主要实现: 使用启用或停用的方式, 提供基本的面向对象的支持(不包括继承, 多态等特征)
注意:
1. 由于 command_not_found_handle 运行于独立的执行环境, 在引发错误的 shell 中
定义的变量可读不可写
2. 基于上述原因
1) 如果类中将字段直接定义为指向对象外部变量的引用(或者保存该变量的名称), 可能会导致读写数据失败.
2) 字段更新比较艰难(目前需要借助文件)
3) 调用导致属性改变的实例方法后, 正确的属性值只保留在文件中, 下次的实例方法调用, 会
先从文件中读取正确值. 但 echo \$obj 的结果可能不是最新值. 作为补救, 模块中默认实现了
toString 和 sync_data 方法, 可返回其最新值, 同时, 类定义中还可以重写这些方法. 推荐
重写 toString 即可, sync_data 最好不要动.
bash 文档相关说明:
https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/bash.html
it is invoked in a separate execution environment with the original command
and the original command's arguments as its arguments
函数:
enable_oop <false | anyelse_include_empty>
SUMMARY
###################################################################################################
:<<COMMENT
启用或停用面向对象编程.
$1: 可用值为任意字符(串), $1 == false, 表示停用; 其他(包括空)表示启用
用法: enable_oop <false | anyelse_include_empty>
注意:
1. 对每个类的要求:
1). 在类定义的末端, 添加:
_class_transform_function --fields "... ..." "$@"
其中, --fields "... ..." 配置需要持久化到对象中的字段名, 例如 --fields "name age career" ,
注意表示 0 个字段应该最少包含一个空格, 例如 --fields " ", 而不能是 --fields ""
2. 将 _create_obj / _perform_method / _class_transform_function / _write_object / _read_object 定义为内部函数,
目的保证默认状态(未启动 oop 时), 这些函数不可用.
COMMENT
enable_oop(){
# 将对象写入文件
# --obj-name: 对象名称, 必须. new 对象时, 无对象名, 应该设置为空格而非空字符 " "
# --class-name: 类名称, obj-name 非空时, 该选项被忽略
# --field-names: 字段名称列表组成的字符串, 以空格相隔, 必须. 如果无字段(属性), 则为空字符而非空字符 " "
# --var-name: 将写入文件的 json 字符串, 也保存为该名称的变量. 可选
# 用法: _write_object --obj-name "..." --class-name "..." --field-names "..." --file-name "..."
# 注意:
# 1. 各个字段的值, 在调用端已经配置好.
_write_object(){
local obj_name class_name field_names var_name # file_name
eval $PASX
params obj-name class-name field-names var_name # file-name
# 1. 确定 class 和 id
local class id
if [ -z "$obj_name" ]; then
# 新建对象
class=$class_name
id=$(random_string)
else
# 已有对象, 分已有记录和没有记录两种情况
class=$(echox "${!obj_name}" | jq -r ".class")
id=$(echox "${!obj_name}" | jq -r ".id")
fi
# 准备 json 记录
local v_n json="{\"class\":\"$class\", \"id\":\"$id\", \"data\":{"
for v_n in $field_names; do
json+="\"$v_n\":\"${!v_n}\","
done
# 如果对象没有字段, 则当前 json 字串的末尾不会是逗号
[ "${json: -1}" == ',' ] && json=${json%?} # -1 前的空格必不可少
json+="}}"
# 如果存在旧记录且不等于新纪录, 则替换之; 不存在旧记录则新建一条记录; 其他情况, 忽略操作
local old_rec=$(grep "$id" $OBJS_FILENAME)
if [ "$old_rec" ]; then
[ "$old_rec" != "$json" ] && sed -i "s/^.*$id.*$/$json/" $OBJS_FILENAME
else
# 不存在旧记录, 则直接添加
echox "$json" >> $OBJS_FILENAME
fi
# 赋值, 供调用端使用
if check_var_name "$var_name"; then
local -n ref_obj=$var_name
ref_obj="$json"
fi
}
# 从文件读取对象
# $1: 对象名称, 必须
# 用法: read_objec <object_name>
_read_object(){
if [ "$1" ]; then
local -n ref_obj=$1
local id=$(echox "$ref_obj" | jq -r ".id")
grep "$id" $OBJS_FILENAME
fi
}
# new 对象使用的函数体. 其中的 $1 $2 ... 编号, 是针对 command_not_found_handle 函数的参数
# 例如, 创建对象语句是 new Person bill 28 US 则:
# $1: new
# $2: 类名称即 Person (使用 function 定义)
# $3 及以后: 构造函数需要的所有参数
_create_obj(){
if declare -f $2 &>/dev/null; then
func=$2
shift 2
$func "$@"
else
log_error "$2 class undefined"
return 120
fi
}
# 执行类或对象方法使用的函数体. 其中的 $1 $2 ... 编号, 是针对 command_not_found_handle 函数的参数
# 例如,
# 1. 执行静态方法(其实是以静态的方式执行实例方法, 因为我们目前无法有效区分静态与非静态)的语句:
# Person.say hello world, 则
# $1="Person.say"
# $2 及以后为方法需要的所有参数
# 而 类名称 inst=Person ; 类方法 meth="say"
# 2. 执行实例方法的语句 john.say hello world 则
# $1="john.say",
# $2 及以后为方法需要的所有参数
# 而 对象实例 inst=john ; 对象方法 meth="say"
# 以上两种调用情况, inst 和 meth 均从 $1 解析得到
_perform_method(){
local inst=${1%.*}
local meth=${1#*.}
shift
if declare -f $inst &>/dev/null; then
# 调用静态方法
$inst --method $meth "$@"
elif declare -p $inst &>/dev/null; then
# 调用实例方法
func=$(echo "${!inst}" | jq -r ".class" 2>/dev/null)
if [ "$func" ] && declare -f $func &>/dev/null; then
$func --method $meth --instance $inst "$@"
else
local msg
[ -z "$func" ] && msg="The class is not identified internally within the variable" \
|| msg="The class $func is undefined"
log_error $msg
return 125
fi
else
log_error "$inst is not a class, or a variable."
return 121
fi
}
# 将对象的方法调用, 转化为函数调用
# --fields: 私有变量名称列表
# 其他: 传递给类的方法的所有参数, 可能是:
# 1) "$@" (new 实例)
# 2) --method $meth "$@" (静态方法调用)
# 3) --method $meth --instance $prefix "$@" (实例方法调用)
# 其中 "$@" 是传递给方法的所有参数
# 用法: _class_transform_function --fields "... ..." "$@"
# 仅用于添加到类定义的最后一行, 作为视角方法到实际的内部函数之间的转移
_class_transform_function(){
local fields instance method
eval $PASX
params "fields" "instance" "method"
if [ "$instance" -a "$method" ]; then
if declare -f $method &>/dev/null; then
# 调用已定义的实例方法
# instance 变量保存的是对象名
local -n ref_inst=$instance
# 实例函数
# 1. 从文件中获取最新值,
ref_inst=$(_read_object $instance) # $OBJS_FILENAME
# 2. 字段赋值
local fd
for fd in $fields; do
local -n ref_v=$fd
ref_v=$(echo "$ref_inst" | jq -r ".data.$fd")
done
# 3. 调用. 在方法的实际参数前有 --fields ".." --instance "..." --method "..." 共六个参数
shift 6
$method "$@"
# 4. 上述调用, 可能已经修改字段, 所以需要更新 instance 携带的字段
# 通过引用修改的结果, 仅在 command_not_found_handle 中能看到
# 通过 --var-name $instance 修改无效
_write_object --obj-name $instance --field-names "$fields" # --var-name $instance --file-name $OBJS_FILENAME
elif s_ct_w $method toString sync_data; then
# 未定义的方法中, 需要单独处理 toString sync_data, 作为其默认实现
# _read_object $instance | jq -C --indent 4
_read_object $instance
else
# 其他未定义, 则记录错误
log_error "method $method undefined."
return 123
fi
elif [ -z "$instance" -a -z "$method" ]; then
if declare -f ctor &>/dev/null; then
# 调用构造器
shift 2 #
ctor "$@"
local self
_write_object --class-name ${FUNCNAME[1]} --field-names "$fields" --var-name self # --file-name $OBJS_FILENAME
echox $self
else
# 未定义构造器, 记录错误
log_error "contructor of ${FUNCNAME[1]} class not found."
return 122
fi
elif [ -z "$instance" -a "$method" ]; then
# 静态函数. 在方法的实际参数前有 --fields ".." --method "..." 共四个参数
shift 4
$method "$@"
fi
}
local -r REG_NEW='^new$'
local -r REG_METH='^[_a-zA-Z][_0-9a-zA-z]*\.[_a-zA-Z][_0-9a-zA-z]+$'
! declare -p OBJS_FILENAME &>/null && declare -gr OBJS_FILENAME='/oop-cache/objects.rec'
if [ "$1" == false ]; then
unregister_command_not_found_handler $REG_NEW $REG_METH
unset -f _class_transform_function _perform_method _create_obj _read_object _write_object
rm -f $OBJS_FILENAME
else
# 将 new 对象和执行类/对象方法的 command_not_found_handler 注册到
# command_not_found_handle 中
register_command_not_found_handler \
"$REG_NEW '$(f_body _create_obj)'" \
"$REG_METH '$(f_body _perform_method)'"
ensure_par $OBJS_FILENAME
touch $OBJS_FILENAME
fi
}
该模块只包含一个函数(其余均为嵌套函数) enable_oop, 用于启动或停用面向对象编程. 基本思路是, 根据参数是否是 false, 停用或启用面向对象. 注意 echo $obj 的结果可能不是最新值, 但并不影响任何实例方法调用结果的正确性.
【测试1】
现在试试”动机”里的代码:
Person(){
local name age career
ctor(){
name=$1
age=$2
career=$3
}
say_hello(){
aop tip center "hello, my name is $name, I am $age years old, I am a $career."
info "these are other parameters:<$1>,<$2>,<$3>..."
}
set_age(){
age=$1
}
to_string(){
echox "name:$name, age:$age, carrer:$career. class:Person"
}
get_age(){
echox $age
}
# 必须添加的一行
_class_transform_function --fields "name age career" "$@"
}
clear
# 启用面向对象
enable_oop
local p=$(new Person "John williams" 153 "guitar artist")
aop info right "1. call method as static..."
Person.say_hello here there where
aop info right "2. modify age to 92, then call say_hello..."
p.set_age 92
p.say_hello one two three
aop info right "3. echo object may be incorrect..."
echo "\$p is incorrect :<$p>"
aop info right "4. using toString or sync_data makes correct:"
p.toString
p.sync_data
aop info right "5. now diable oop..."
enable_oop false
pushee
set +e
local p2=$(new Person "Blim" 72 "basketball player")
p2.say_hello first second third
popee运行结果如下:
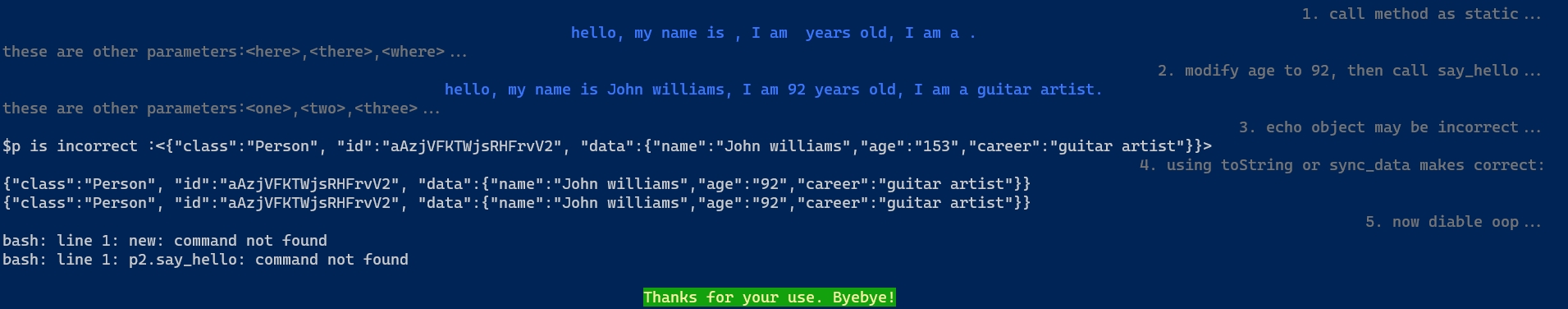
可见, 面向对象的启用和停用函数 enable_oop 已起作用.
【测试2】
主要针对修改属性(字段)的操作, 静态方式调用方法, 以及使用错误的对象引用调用方法的测试.
way4(){
# --method
#
Person(){
local name age career
ctor(){
name=$1
age=$2
career=$3
}
say_hello(){
aop tip center "hello, my name is $name, I am $age years old, I am a $career."
info "these are other parameters:<$1>,<$2>,<$3>..."
}
# 注意涉及修改字段的方法, 调用后应立即调用 ud_var, 以便字段数据同步
set_age(){
age=$1
}
set_name(){
name=$1
}
set_career(){
career=$1
}
another_way(){
info "another_way is called. parameter information :"
local idx
for idx in $(seq 1 $#); do
menu "[$idx]=<${!idx}>"
done
}
example_named_parameter(){
local alive slap swim grap
eval $PASX
local all_pos=$(params)
params "'alive a' yes no" \
" slap china" \
"'---swim s' here there" \
"'grap ---g' 234 889"
echox "alive=<$alive>, slap=<$slap>, swim=<$swim>, grap=<$grap>"
echox "all postion parameters:"
info -e $all_pos
tip "instance fields:"
info "name:<$name>,age:<$age>,career:<$career>"
}
# 重写默认的 toString 方法
toString(){
echox "class:Person; name=$name, age=$age, career=$career"
}
# 每个类定义的最后, 均需要这一行. 其中 --fields 参数, 根据实际情况修改
_class_transform_function --fields "name age career" "$@"
}
aop caption center "1. 启用面向对象, 并创建对象"
enable_oop
local pkm=$(new Person "Jhon Willimas" 69 "guitar artist")
aop caption center "2.调用只读方法"
pkm.say_hello "one two " three "four five six.... "
pkm.another_way "hello world" 234 998 -15.4 " you win " "etc ... ... "
pkm.example_named_parameter one -s two -g 123 -a 'hello world' "查找构造函数的IL代码。" \
"The Dow Jones Industrial Average closed down 2.5%" ------------swim " Despite widespread market expectations that AP "
aop caption center "3. 调用写方法"
pkm.set_age 77
pkm.set_name Blim
pkm.set_career "common worker"
pkm.say_hello "update successfully ! " " you win " " they lose "
aop caption center "4. 如果上述 2 的方法, 以静态方式调用, 则实例字段全部为空"
Person.example_named_parameter one -s two -g 123 -----a 'hello world' -alive ' welcome to our company !' "查找构造函数的IL代码。" \
"The Dow Jones Industrial Average closed down 2.5%" ------------swim " Despite widespread market expectations that AP "
aop caption center "5. 重写的 toString 方法"
notice "override toString:<$(pkm.toString)>"
pushee
set +e
aop caption center "6. 手工触发错误: 未定义方法 / 对象错误(未定义类型) / 对象错误(非对象), 请查看 error.log"
pkm.no_such_method
local mkt="{\"class\":\"slim\"}"
mkt.say_hello "this is " a " null reference"
local pay="hello"
pay.say_hello "this is" a "object"
aop caption center "7. 停用面向对象, 再尝试创建对象, 调用方法, 则恢复原来的报错"
enable_oop false
local ppk=$(new Person "oli gan" 22 "basketball player")
ppk.say_hello
pkm.say_hello
popee
}
clear
way4运行结果如下:
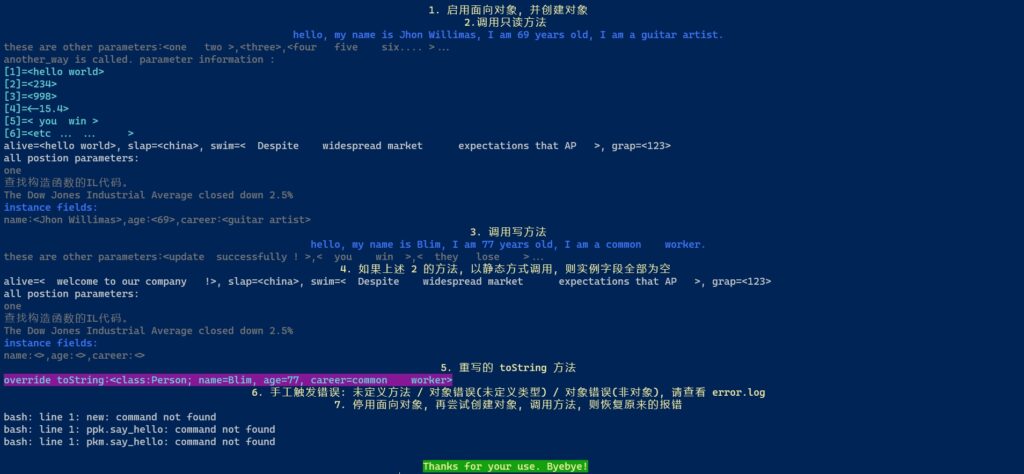
注意:
- 重写的 toString 方法已经生效; 如果在类定义中注释掉该方法, 默认的返回 json 字符串的默认方法将浮出水面.
- enable_oop false 后, error.log 写入以下日志(注意应事先保证 set +e, 否则从第二个起的错误将没有机会展示):
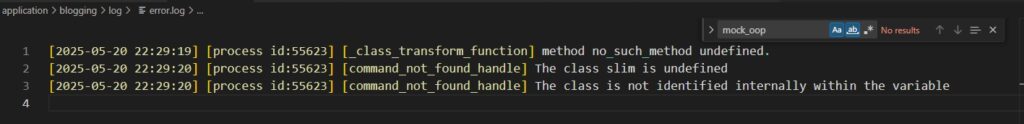
【测试3】
示范在对象中如何嵌套数组和其他对象, 以及修改这些数组和对象失效的问题.
way14(){
Person(){
local name age
ctor(){
name=$1
age=$2
}
update(){
name="$name ==> $1"
age="$age ==> $2"
}
_class_transform_function --fields "name age" "$@"
}
Class(){
local n_students n_head_teacher
ctor(){
n_students=$1
n_head_teacher=$2
}
# $1: key
# $2: student object name
# 注意: 在 command_not_found 函数内部修改外部变量(arr_stu)无效
add_student(){
local -n ref_stus=$n_students
ref_stus+=([$1]=$2)
# eval "$n_students+=([$1]=$2)"
#describe_array arr_stu --item-is-name
}
get_students_name(){
echox $n_students
}
get_head_teacher_name(){
echox $n_head_teacher
}
_class_transform_function --fields "n_students n_head_teacher" "$@"
}
enable_oop
local stu1=$(new Person John 15)
local stu2=$(new Person Mary 16)
local stu3=$(new Person Luice 17)
local -A arr_stu=([one]=stu1 [two]=stu2 [three]=stu3)
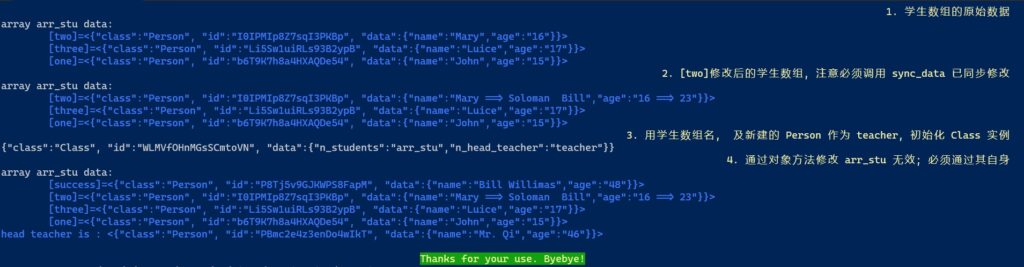
aop caption right "1. 学生数组的原始数据"
describe_array arr_stu --item-is-name
aop caption right "2. [two]修改后的学生数组, 注意必须调用 sync_data 已同步修改"
stu2.update "Soloman Bill" 23
stu2=$(stu2.sync_data)
describe_array arr_stu --item-is-name
aop caption right "3. 用学生数组名, 及新建的 Person 作为 teacher, 初始化 Class 实例"
local teacher=$(new Person "Mr. Qi" 46)
local fasts=$(new Class arr_stu teacher)
fasts.toString
aop caption right "4. 通过对象方法修改 arr_stu 无效; 必须通过其自身"
local new_stu=$(new Person "Bill Willimas" 48)
fasts.add_student five new_stu
arr_stu+=([success]=new_stu)
local arr_stu_name=$(fasts.get_students_name)
describe_array $arr_stu_name --item-is-name
local tea_name=$(fasts.get_head_teacher_name)
tip "head teacher is : <${!tea_name}>"
enable_oop false
}
clear
way14运行结果:
【未完】
很明显, 这里的面向对象, 仅仅是简单实现. 因为面向对象的太多特点, 例如继承, 多态, 虚函数, 接口等等, 鉴于时间关系, 暂时无法实现. 有兴趣的朋友, 欢迎对此进行扩展! 当然, 如果某一天 bash 新版本在语法层面自己实现了面向对象, 这里做的所有工作就多余了呵.
该对象模块 oop.sh, 在脚本的瘦身以及编译脚本为可执行体中, 有具体应用.
谢谢观看!