【动机】
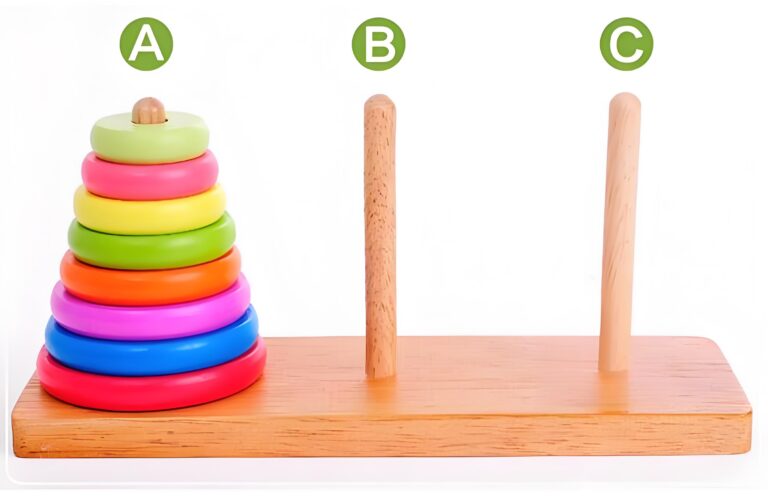
汉诺塔问题家喻户晓,是递归函数的简单应用,大部分的实现都是强调算法,表示盘子的移动几乎都是用的 A->B B-C 之类的符号来表示盘子的移动过程。如何在 linux shell 字符界面形象的演示盘子的移动呢?
【意图】
- 用一个(和多个)带前景色的空格表示盘子,通过连续的擦除、绘制该盘子,表示盘子的移动;
- 在盘子的擦除、绘制过程中,还要保证当前杆不受影响(通过重绘的方式);
- 杆数量可配置(最少为3),方便将来扩展;
- 每根杆可容纳的盘子最大数量, 与杆的数量、屏幕高度、屏幕宽度、杆的间隙均有关系;
- 每根杆需要自己的数据结构(数组),已保存当前的盘子状态;
- 运行前的用户配置:杆数量、盘子数量、移动顺序;
- 运行过程中的简单交互:任意键暂停(继续),ctrl+c 优雅退出(不同于 ctrl+z 的强制退出);
- 通过日至记录移动过程;
- 等等… …
【实现】
这里只展示入口脚本 main.sh,以及 UI 驱动部分的脚本 hanoi.sh。 完整的打包代码,可参看源码下载。
- main.sh
#!/bin/bash
set -e
# global constant:
declare -r __DEBUG__=
declare -r ENTRY_FILE_PATH=$(readlink -f $0)
declare -r ENTRY_FILE_NAME=$(basename $ENTRY_FILE_PATH)
declare -r ROOT_DIR_PATH=$(dirname $ENTRY_FILE_PATH)
declare -r ROOT_DIR_NAME=$(basename $ROOT_DIR_PATH)
# region Ignored
# 根据当前脚本与 library 和 execution 的相对位置, .. 可能有所变化
declare -r LNX_LIB_DIR="$ROOT_DIR_PATH/../../library"
# endregion Ignored
# 块 source, 详情查看 library/doc/compile.txt
# region Sourcing
for file in \
$(find $ROOT_DIR_PATH \
-path "$ROOT_DIR_PATH/document" -prune -o \
-type f -regex .*?\.sh$ \
-not -wholename "$ENTRY_FILE_PATH" \
-print ) \
$(find $LNX_LIB_DIR \
-type f -regex .*?\.sh$ ) ; do
source $file
done
# endregion Sourcing
# -------------------------------start ---------------------------------
__TEST__=
[ -z "$__TEST__" ] && hanoi || test_start
# region Ignored
if [ "$1" ]; then
menu "start compiling ..."
# 极简调用方式, 但要注意将源文件的 compiling 块和 soucing 块的名称写成函数默认, 即 Ignored 和 Sourcing:
cmdline="script2execution
--target-path \"$ROOT_DIR_PATH/../../execution/$ROOT_DIR_NAME/${ENTRY_FILE_NAME%.*}\"
--attaches \"log\"
"
perform --prompt "编译中, 请稍候......" --cmdline "$cmdline" --delay 0.2 --erase
tip "Congratulaions. file compiled."
aop "success -e" center "Thanks for your use. Byebye!"
fi
# endregion Ignored注意,带任意命令行参数,表示运行完毕立即编译自身为可执行体(相关说明参见编译)。
2. hanoi.sh
#!/bin/bash
:<<SUMMARY
rely:
1. common/*.sh
2. pedestal.sh
3. pole.sh
4. plate.sh
5. scence.sh
6. animator.sh
hanoi.sh 将汉诺塔问题, 以图形动画的方式展示
1. 命令行问答式输入汉诺塔参数: 杆数量, 盘数量, 移动方式
2. 配置光标的隐显
3. 配置 ctrl + c 中断
4. 配置 屏幕尺寸变化中断
5. 配置动画的任意键暂停/继续
6. 统计一共经过几步(移动几次)
函数:
config_trap
cancel_trap
config_data
user_command <cmd_flag>
ready
move
moving
final
hanoi
SUMMARY
#--------------------------------常数列表----------------------------
#pc=
#plates=
g_start_pole=
g_by_plole=
g_end_pole=
g_user_exit_prompt=
g_move_times=0
#-----------------------pole----------------------
config_trap(){
trap "user_command ctrl-cz" INT # TSTP
trap "user_command scr-ch" WINCH
}
cancel_trap(){
trap -- INT
# trap -- TSTP
trap -- WINCH
}
config_data(){
# 杆的数量与基座数量永远一致
local pc plates pole_max_count=$(ped_max_amount)
read -p "请输入杆的数量[3-$pole_max_count](输入非法值, 则采用默认 3): " pc
pc=$(ensure_availabel_integer ${pc:=-1} 3 3 $pole_max_count)
#echo "<$pc>"
read -p "请输入起始杆编号[1-$pc](输入非法值, 则采用默认 1): " g_start_pole
g_start_pole=$(ensure_availabel_integer ${g_start_pole:=-1} 1 1 $pc)
#echo "<$g_start_pole>"
read -p "请输入过渡杆编号[1-$pc, 除 $g_start_pole 以外](输入非法值, 则采用随机值): " g_pole_by
# 设置 start 为默认值, 以便在输入值非法, 启动该默认值, 继而触发随机值的产生
g_pole_by=$(ensure_availabel_integer ${g_pole_by:=-1} $g_start_pole 1 $pc $g_start_pole)
#echo "<$g_pole_by>"
read -p "请输入终点杆编号[1-$pc, 除 $g_start_pole 和 $g_pole_by 以外](输入非法值, 则采用随机值): " g_pole_end
g_pole_end=$(ensure_availabel_integer ${g_pole_end:=-1} $g_start_pole 1 $pc $g_start_pole $g_pole_by)
#echo "<$g_pole_end>"
ped_count $pc
local plt_max_count=$(plt_max_amount)
read -p "请输入盘子数量[1-$plt_max_count](输入非法值, 则采用最大值 $plt_max_count): " plates
plates=$(ensure_availabel_integer ${plates:=-1} $plt_max_count 1 $plt_max_count)
#echo "<$plates>"
plt_amount $plates
local user_sure
local dir="$g_start_pole ==> $g_pole_by ==> $g_pole_end"
read -p "请核对您输入的数据: 杆数量 $pc, 盘数量 $plates, 移动方向 $dir. 按 r 重新设置, 其他键开始...." -n 1 user_sure
if [ "$user_sure" == "r" -o "$user_sure" == "R" ]; then
echo
config_data
else
local orig_txt=$(title_text)
title_text "$orig_txt: $dir ($plates)"
fi
}
# $1: cmd_flag
user_command(){
case $1 in
ctrl-cz)
g_user_exit_prompt="You interrupt the app."
#
;;
scr-ch)
g_user_exit_prompt="Screen size changed. You need probably restart hanoi."
;;
*)
g_user_exit_prompt="unknow error cause to finish the app.";;
esac
final
}
ready(){
config_trap
config_data
#tput init
tput civis # 隐藏光标
snc_open
anim_ready_plates $g_start_pole
}
# $1: plate amount
# $2: start_pole
# $3: by_pole
# $4: end_pole
move(){
local hep=$[$1-1]
if [ $1 -eq 1 ]; then
log_info "hanoi: <$2>===><$4>"
anim_plate_pole_to_pole $2 $4
let g_move_times++
else
move $hep $2 $4 $3
move 1 $2 $3 $4
move $hep $3 $2 $4
fi
}
# 为了记录移动次数
moving(){
move $(plt_amount) $g_start_pole $g_pole_by $g_pole_end
g_user_exit_prompt="Complete! Total move times: $g_move_times."
final
}
final(){
snc_close "$g_user_exit_prompt"
cancel_trap
#tput cnorm # 恢复光标
echo -e "\e[?25h"
aop tip center "Thank you for your using"
}
hanoi(){
ready
sleep 3
moving &
key_to_pause_resume_process $!
}【测试】
为简单起见,设置盘数量为 4,效果如下:
【后记】
该源码完成时间比较早,采用的仅仅是模块化的结构,还可以考虑重写成面向对象的形式。